
Refraction and Dispersion of Light is an important chapter in Class 8 DAV Science textbook. This chapter explains how light travels from one medium to another. It also shows the ray diagrams for different positions of objects and image formed. If you have any doubt regarding DAV class 8 Science Chapter 10 Question answers feel free to reach out to us through the comments section. Let us check out the DAV Dispersion and Refraction of Light solutions.
A. Fill in the Blanks
1. A ray of light, passing from one medium to another, does not bend its path if its angle of incidence equals ___________ degree.
2. The more is the optical density of a given medium, the ___________ is the speed of light through it.
3. The phenomenon of the splitting of white light into seven colours is known as the phenomenon of ___________.
4. The point, on the principal axis of a concave lens, from where a beam of incident parallel ray appears to diverge, is called the ___________ of the concave lens.
5. An object should be placed at the ___________ point so that a convex lens forms its real and inverted image of the same size.
Answer: (1) 0 (2) less (3) dispersion of light (4) focus (5) 2F
B. Write True or False for the following statements
1. The basic cause of refraction is the change in the speed of light as it goes from one medium to another.
2. In an optically denser medium, the speed of light is more than the speed of light in vacuum.
3. An (obliquely) incident ray always bends away from the normal when it passes from one transparent medium into another.
4. A coin, kept at the bottom of an empty dry cup, appears to rise up’ when some water is poured into the cup.
5. When white light is ‘dispersed’ by a glass prism, the yellow colour in it, bends more than the blue colour.
Answer: (1) True (2) False (3) False (4) True (5) False
C. Tick the Correct option
1. Which of the following conditions is not necessary for a change in the direction of propagation when a light ray goes from one medium to another?
Answer: The incident light rays must always have only the blue colour.
2. Which of the following diagrams correctly shows the ‘bending of a light ray’ as it goes from an optically denser medium into an optically rarer medium?
Answer: Option B is the correct option.
3. The angle, between the incident ray and the emergent ray, for a rectangular glass slab is-
Answer: 0⁰ is the right answer.
4. Which of the following figures correctly represents the passage of white light through a glass prism?
Ans: Option C will be the correct option.
5. An incident ray, passing through the optical centre of a concave lens, after refraction through it, will-
Answer: The incident ray will go undeviated after refraction.
6. When an object approaches a convex lens, from infinity towards its focus, the image, formed by it-
Answer: keeps on shifting away from the lens.
7. Tanya’s grandmother needs a lens to read small letters in her book. For this she should use-
Answer: Tanya’s grandmother should use a concave lens, The distance should be less than its focal length.
D. Answer the following questions in brief.
1. Light propagates faster through a Medium A than through another Medium B.
(a) Which of the two media has a higher optical density?
Answer: Medium B has higher optical density.
(b) State the condition under which no ‘change in the direction of propagation’ of a light ray would take place when it passes from Medium A to Medium B.
Answer: No change will occur when the incident ray makes a right angle at the point of incidence.
2. Why does a pencil appear bent when it is partially dipped in water?
Answer: There is a change of medium when the light rays travel from water to air. When light rays coming from water enter the air, they bend away from normal. Due to this, light rays appear to be coming from a different position than the actual position of the pencil. This makes the pencil appear bent when looked from outside the glass.
3. Trace the path of rays in the following ray diagrams:
4. When a spherical lens is held towards the Sun and a sharp image is formed on a piece of black paper, a hole gets burnt in the black paper, after some time.
(a) Name the lens used in the above activity.
Answer: Convex lens is used for the above experiment.
(b) What name is given to the distance between the spherical lens and the black paper?
Answer: The distance between the Spherical lens and the black paper is the Focal length.
(c) What is the relative advantage of using a black paper rather than a white paper?
Black colour absorbs more energy as compared to white colour. The black paper absorbs more heat energy and the paper burns faster as compared to the white paper.
5. What kind of lens would form
(a) an inverted and magnified image of the object?
Answer: Convex lens will form a magnified and inverted image of the object.
(b) an erect and magnified image of the object?
Answer: Convex lens forms an erect and magnified image of the object.
c) an inverted and diminished image of the object?
Answer: Convex lens.
(d) an erect and diminished image of the object?
Answer: Concave lens
6. Draw labelled ray diagrams to illustrate the differences between the virtual images formed by using (a) a concave lens (b) a convex lens.
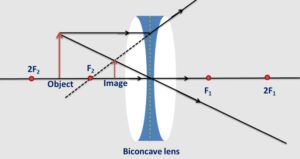

E. Answer the following questions
1. A coin is placed at the bottom of a clear glass vessel. An observer moves herself to a position where the coin goes just out of sight of her eyes. Keeping her eyes in that position, she asks her friend to pour some water, gradually into the glass vessel.
(a) What would she observe?
Answer: Coin will be visible to her when water will be poured in the glass.
(b) Name the phenomenon involved in this observation.
Answer: Refraction of light is the phenomenon involved in this.
(c) Draw a neat labelled diagram to justify your answer.
Check your book for the diagram

Leave a Reply